predict and margins: A Substantive Example1 Mar 2021 08:09:03
Odds ratios, or coefficients showing the association of the independent variables with the log odds, represent the most immediate output of a logistic regression. However, for a variety of reasons, it may make sense to not only report odds ratios, but also to investigate predicted probabilities.
The data are an extract of the National Survey of Children’s Health, 2018. The data contain information on children’s current depression status, their exposure to various Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs) and their sex and race.
. clear all
. cd "/Users/agrogan/Desktop/newstuff/categorical/predict-and-margins-substantive-example" /Users/agrogan/Desktop/newstuff/categorical/predict-and-margins-substantive-example
. use "NSCH_ACES.dta", clear
. describe depress ace1R ace3R ace4R ace5R ace6R ace7R ace8R ace9R
storage display value
variable name type format label variable label
──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
depress byte %9.0g RECODE of k2q32b (Depression Currently)
ace1R byte %9.0g RECODE of ace1 (Hard to Cover Basics Like Food or
Housing)
ace3R byte %9.0g RECODE of ace3 (Child Experienced - Parent or Guardian
Divorced)
ace4R byte %9.0g RECODE of ace4 (Child Experienced - Parent or Guardian
Died)
ace5R byte %9.0g RECODE of ace5 (Child Experienced - Parent or Guardian
Time in Jail)
ace6R byte %9.0g RECODE of ace6 (Child Experienced - Adults Slap, Hit,
Kick, Punch Others)
ace7R byte %9.0g RECODE of ace7 (Child Experienced - Victim of Violence)
ace8R byte %9.0g RECODE of ace8 (Child Experienced - Lived with Mentally
Ill)
ace9R byte %9.0g RECODE of ace9 (Child Experienced - Lived with Person
with Alcohol/Drug Problem)
We estimate a logistic regression using ,or to ask for odds ratios.
. logit depress ace1R ace3R ace4R ace5R ace6R ace7R ace8R ace9R i.sc_race_r i.sc_sex, or
Iteration 0: log likelihood = -760.76202
Iteration 1: log likelihood = -739.43605
Iteration 2: log likelihood = -739.012
Iteration 3: log likelihood = -739.01149
Iteration 4: log likelihood = -739.01149
Logistic regression Number of obs = 1,442
LR chi2(15) = 43.50
Prob > chi2 = 0.0001
Log likelihood = -739.01149 Pseudo R2 = 0.0286
────────────────────────────────────┬────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
depress │ Odds Ratio Std. Err. z P>|z| [95% Conf. Interval]
────────────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
ace1R │ 1.275539 .177745 1.75 0.081 .970688 1.67613
ace3R │ .8328396 .1225773 -1.24 0.214 .6241393 1.111325
ace4R │ 1.03589 .2559531 0.14 0.887 .6382551 1.681253
ace5R │ 1.238661 .2620121 1.01 0.312 .8182749 1.87502
ace6R │ 1.242079 .284433 0.95 0.344 .7929142 1.945684
ace7R │ 1.438336 .3249996 1.61 0.108 .9236915 2.23972
ace8R │ 1.931751 .3179664 4.00 0.000 1.399082 2.667221
ace9R │ .6476801 .1088199 -2.59 0.010 .4659572 .9002747
│
sc_race_r │
Black or African American alone │ 1.150371 .3258065 0.49 0.621 .6603312 2.004075
American Indian or Alaska Native.. │ .7002442 .4236335 -0.59 0.556 .213939 2.291971
Asian alone │ 1.222781 .5325791 0.46 0.644 .5207269 2.871358
Native Hawaiian and Other Pacifi.. │ .2318806 .3550441 -0.95 0.340 .0115331 4.662103
Some Other Race alone │ .7923493 .3360807 -0.55 0.583 .3450431 1.819533
Two or More Races │ .7852821 .1983556 -0.96 0.339 .4786515 1.288345
│
sc_sex │
Female │ 1.36572 .1769313 2.41 0.016 1.059466 1.760501
_cons │ 2.357814 .3247614 6.23 0.000 1.799975 3.088536
────────────────────────────────────┴────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
Note: _cons estimates baseline odds.
Predicted probabilities are each participant’s individual predicted probability of experiencing depression based upon the independent variables included in the model. We often denote such predicted probabilities with \(\hat{y}\)
. predict yhat (option pr assumed; Pr(depress)) (1,558 missing values generated)
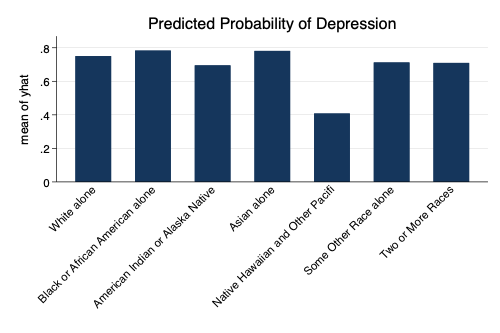
yhat is a variable in the data, just like any other variable, and we can tabulate and graph it.
. tabulate sc_race_r, summarize(yhat)
Race of │
Selected │
Child, │ Summary of Pr(depress)
Detailed │ Mean Std. Dev. Freq.
────────────┼────────────────────────────────────
White alo │ .75045109 .05197594 22,445
Black or │ .78322165 .04940146 1,881
American │ .69508786 .07204945 235
Asian alo │ .78128584 .03714901 1,377
Native Ha │ .40799774 .06911794 73
Some Othe │ .71235484 .05558899 763
Two or Mo │ .70971281 .06233783 2,198
────────────┼────────────────────────────────────
Total │ .74863835 .05781597 28,972
. graph bar yhat, ///
> over(sc_race_r, label(angle(forty_five))) ///
> title("Predicted Probability of Depression") ///
> scheme(michigan)
. graph export mybar.png, width(500) replace (file /Users/agrogan/Desktop/newstuff/categorical/predict-and-margins-substantive-example/mybar.png wr > itten in PNG format)

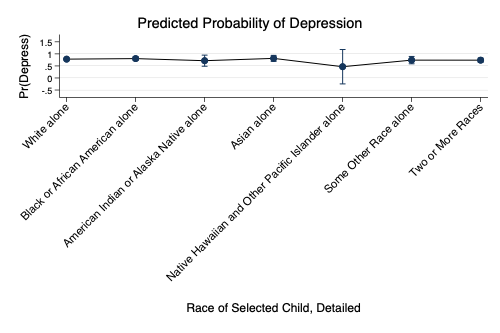
In their simplest form, predictive margins are average predicted probabilities were everyone in the sample were treated as if they were of a particular race.
. margins sc_race_r // predictive margins
Predictive margins Number of obs = 1,442
Model VCE : OIM
Expression : Pr(depress), predict()
────────────────────────────────────┬────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
│ Delta-method
│ Margin Std. Err. z P>|z| [95% Conf. Interval]
────────────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
sc_race_r │
White alone │ .7819423 .011883 65.80 0.000 .758652 .8052326
Black or African American alone │ .8043012 .0419853 19.16 0.000 .7220115 .8865909
American Indian or Alaska Native.. │ .7173792 .1176945 6.10 0.000 .4867023 .9480561
Asian alone │ .8135006 .0635869 12.79 0.000 .6888727 .9381286
Native Hawaiian and Other Pacifi.. │ .4675318 .3641302 1.28 0.199 -.2461503 1.181214
Some Other Race alone │ .7409869 .0777287 9.53 0.000 .5886414 .8933323
Two or More Races │ .7393176 .0451682 16.37 0.000 .6507896 .8278456
────────────────────────────────────┴────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
We could also evaluate
marginsholding other variables at their mean values using theatmeansoption. You can also read about obtainingmarginsfor various combinations of the independent variables by typinghelp marginsat the Stata prompt.
The essential graphing command is marginsplot, which will usually produce a perfectly useable graph. The other graphing options are added for clarification and aesthetic purposes.
. marginsplot, ///
> title("Predicted Probability of Depression") ///
> ylabel(, labsize(small) angle(horizontal)) ///
> xlabel(, angle(forty_five)) ///
> scheme(michigan)
Variables that uniquely identify margins: sc_race_r
. graph export mymargins.png, width(500) replace (file /Users/agrogan/Desktop/newstuff/categorical/predict-and-margins-substantive-example/mymargins.pn > g written in PNG format)